BIM Education Schema or BIM Schema is an educational framework created to reskill the traditional AEC industry, including all the stakeholders of the value networks during the whole lifecycle. The purpose of BIM Education Schema is to support people´s digital transformation process, creating new BIM profiles to support the BIM collaborative technologies and methodologies. BIM represents the ontology/semantic that introduces the traditional AEC industry and transform it in the new digital AECO industry, based on interoperatibility.
BIM Schema was delivered as European BIM Higher Education Framework in june 2.023 by the BIM4ed consortium [bim4ed.com], related with TBKHE Eramus+ project. BIM Education Schema was originally developed by gustavo ferreiro, CEO of BIMfreelance, since 2.011 as a BIM Education Framework, in response to the problematic of a massive BIM skills needed for a successful openBIM adoption. First known as BIM University framework, was originally centered in development of a BIM Skills framework, and soon expanding to BIM abilities. In 2.022 the author declared the BIM Schema as opensource, under cc licence.
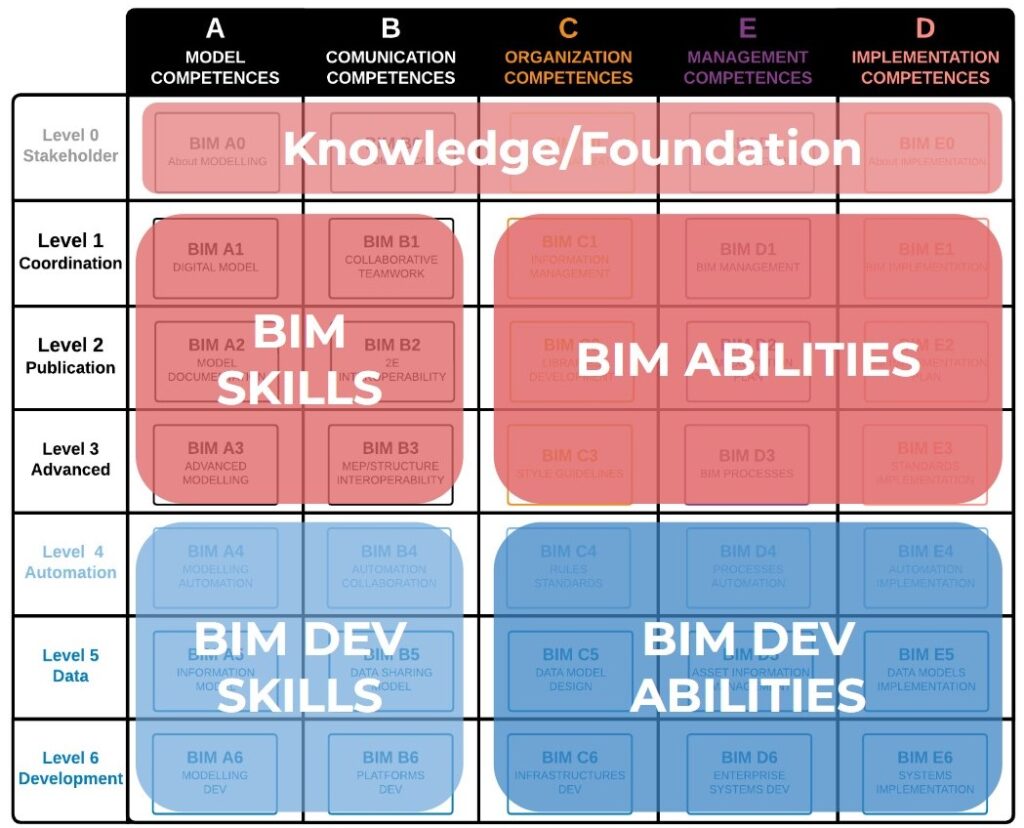
BIM Schema matrix
BIM Education Schema is organized in 6 maturity levels and 7 areas, with 42 courses and 105 microcompetencies, and Includes 20 BIM profiles, 4 sectors and 70 openBIM certified softwares. The BIM Education Schema is a technological framework, that provides accreditation for AECO profiles and also AECO tech profiles.
The matrix relates 2 dimensions: BIM Management competencies, in capital letters, and BIM Development competencies, with numbers. This schema is based on the Bloom Taxonomy, in all it´s ranges, from remember to create (using the most recent modified version)
BIM Management levels:
A Modelling: referred to the process of building information modelling compentencies.
B Communication: referred to collaboration and communication competencies.
C Organization: referred to the expert competencies within the AECO organization.
D Management: referred to the management competencies of a Building Information Modelling project.
E Implementation: referred to the competencies to implement BIM in AECO organizations.
BIM Development levels:
0 Stakeholders: Understanding of all stakeholders about the exchanging of information.
1 Coordination: Competencies to coordinate BIM exchange of information.
2 Delivery: Competencies of how to create and deliver models, representations and other deliverables.
3 Advanced: Advanced competencies for specialized dimensional profiles.
4 Automation: Competencies related with models and processes automation.
5 Data: Competencies in Information Management.
6 Development: Competencies in development of systems, platforms and infrastructures based on BIM.
Each cell represents a Unit or Course. The duration of each course is 30 hours total.
| A Modelling | B Communication | C Organization | D Management | E Implementation | |
| 0 Stakeholders | BIM A0 About Modelling | BIM B0 About Communication | BIM C0 About Organization | BIM D0 About Management | BIM E0 About Implementation |
| 1 Coordination | BIM A1 Digital model | BIM B1 Collaborative Teamwork | BIM C1 Information Manager | BIM D1 BIM Management | BIM E1 BIM Implementation |
| 2 Delivery | BIM A2 Model documentation | BIM B2 2e Interoperability | BIM C2 BIM Style Guidelines | BIM D2 BEP BIM Exectution Plan | BIM E2 BIP BIM Implementation Plan |
| 3 Advanced | BIM A3 Advanced modelling | BIM B3 Advanced Interoperability | BIM C3 Objects development | BIM D3 BIM processes | BIM E3 Standards implementation |
| 4 Automation | BIM A4 Automation modelling | BIM B4 Automation collaboration | BIM C4 Rules Standardization | BIM D4 Processes automation | BIM E4 Automation Implementation |
| 5 Data | BIM A5 Information model | BIM B5 Data sharing | BIM C5 Data Model design | BIM D5 Asset Information Management | BIM E5 Data Models Implementation |
| 6 Development | BIM A6 Modelling Dev | BIM B6 Platforms Dev | BIM C6 Infrastructures Dev | BIM D6 Enterprise systems Dev | BIM E6 Digital Systems implementation |
CPBL based didactic methodology
Then, BIM Schema requires to declare which project/s is used in each course, and the CDE/IDE infrastructures used to develop the project practice during the selected lifecycle phase. Anyway, the guide for openBIM projects is ISO 19650, and as BIM Education Schema is aligned with openBIM standards of buildingSMART International, this is a mandatory requirement.
Multisectoral schema
Then, BIM Schema can be considered a Multisectoral framework, and it is specialy important to create multisectoral profiles for projects like airports, where a lot of domains of IFC are required in a collaborative exchange of information. This also means that a BIM Manager for building sector is only capable to manage BIM building projects, but Multisectoral BIM Managers are required when different sectoral teams collaborate. Of course, IFC is the one that containts all the domains, so the abilities are literaly the same.
BIM competencies and BIM Dev competencies
BIM Education Schema is a digital framework for the whole value chain of the AECO industry, and computer science technologies and methodologies are present as part of the development of the new digital collaborative environments based on interoperability and exchange of information.
Foundation competences of all stakeholders reflects the knowledge and undestanding about the technology and collaborative methodologies during the whole lifecycle of the asset.
BIM competencies are related with AECO profiles, and it is at the most importance the new set of BIM Skills required to model and communicate. Abilities are required by organization´s profiles to manage project´s and asset operations, and how to transform continuously in this innovative environment.
BIM Dev competencies are related with computer science and technologists, and it is demonstrated the advantages of AECO profiles adquiring this competencies and becoming Developers of the systems, platforms and infrastructures required for the whole AECO industry to create value. Deliver the solutions that stakeholders need is at the most importance in this new digital era.
Actually, BIM Schema is easy to use for content creators by using a divide and conquer strategy, and focus on the target group and the level of competencies required at each step of the users´pathway. For example, for Universities, in each degree program, AECO or NON AECO, related with the built environment and AECO industry means and methods, can be used without the need of a complete coordination within the university. Each professor can create contents with the confidence that are solving part of the competencies´puzzle for students, and then, coordinate efforts to complete empty areas.
BIM Qualifications levels
BIM Education Schema clasifies BIM profiles in 5 qualifition levels, identified by stars: Inititial (1 star), BIM Coordinator (2 stars), BIM Modeller (3 stars), BIM Expert (4 stars), Master BIM (5 stars). This BIM education maturity levels related with the BIM profiles are associated with the economic zones´qualifications frameworks. For example, using EQF European Qualification Framework as reference:
☆ 1 star EQF 4 (initial)
☆☆ 2 stars EQF 5 (BIM Coordinator)
☆☆☆ 3 stars EQF 6 (BIM Modeller)
☆☆☆☆ 4 stars EQF 7 (BIM Expert)
☆☆☆☆☆ 5 stars EQF 7 (Master BIM)
BIM Profiles
BIM profiles are a set of AECO professional qualifications awarded during the process of reskilling current AEC professionals. As a result of E&T achievements, each combinations of BIM Schema courses (or Microcredentials) accredited a new BIM profile for the user. BIM profiles are suited as badges to certify that the user achieve the information´s exchange required skills and abilities.
- BIM Stakeholder
- BIM Coordinator
- BIM Architect
- BIM Civil Engineer
- BIM Industrial Engineer
- BIM 2E Engineer
- BIM Structure Engineer
- BIM MEP Engineer
- BIM Sustainability designer
- BIM Project Manager
- BIM Construction Manager
- BIM Quantity Surveyor
- BIM Site Surveyor
- BIM Facility Manager
- BIM Interior Architect
- BIM Expert
- BIM Information Manager
- BIM Manager
- BIM Consultant
Dimensions taxonomy of AECO Industry
Dimensions refer to specific areas of activity that participate in the a physical asset, like a building, factory, highway, airport, etc. Perhaps there is no BIM Management standard that establish this dimensions, there is a basic common understanding that name some of them. As a BIM Education Schema, we propose this list to contribute to the advance and expansion of BIM. The dimensions taxonomy is listed below:
- Modelling
- Collaboration
- 4D – Time
- 5D – Cost
- 6D – Sustainability
- 7D – O&M Operations and Maintenance
- Structures
- MEP
- 9D – Safety & Security
Relationship between BIM uses and BIM Profiles
BIM Uses [1] is set of exchange information profiles established by Penn State University, as part of the most prestigious standard of BIM Execution Plan (BEP). Each BIM Use describes resources and Team competencies required, representing a new dimension for the purpose of E&T in the AECO. Then, BIM Uses are mapped to the BIM Schema units. The complete list and visual presentation of BIM uses mapped to BIM units/courses is available in the BIM Education Schema free course, available in the moodle of this bim4ed consortium LMS [2]
Case Study of international Master BIM Manager
This BIM Schema was used from October 2.014 as the framework for BIM Managers and BIM Consultants by BIMfreelance, in 3 languages and more than 60 countries. The master programs Master BIM Manager, International Master BIM Manager and Global BIM Management mission was create the top BIM Management profiles, resulting in more than 1.200 BIM Managers and Consultants all across the world. This case had a lot of impact in several countries, and demonstrate the impact of BIM education & training in the acceleration of BIM adoption. The case of Spain is paradigmatic, and the comparison with UK adoption strategy is clear: trustable BIM skills are required for the market to proceed to a digital transformation.
Benefits of BIM Education Schema
In general, BIM Education Schema is benefitial for users, goverments and prescriptors (BIM Managers and BIM Consultants)
For the purpose of the business of BIM contents, there are 2 groups that benefit most from BIM Schema: one, Content providers, the value chain owners, and the other, content creators.
- Recognized accreditation
- Easy to use for creators and users
- Competitive advantages for content providers
- Trusted and reliable large number of BIM profiles available for AECO industry
- Acceleration of BIM adoption
BIM Schema concepts
The concepts that are part of the BIM Schema framework are:
- BIM Microcredentials (EU program) Learning Outcomes
- BIM Dimensions
- openBIM Software
- BIM Qualification levels
- BIM uses
- BIM profiles
BIM Topics mapping
One of the main functionalities of BIM Schema is the mapping capabilities of contents, BIM uses, frameworks, topics, etc. The case of the main BIM topics are easy to map from related row and column. For example, concurrent engineering is related with comunication and advanced digital skills, as an advanced interoperability process developed by engineering modellers. Note the importance of this BIM topics for the process of accreditation and certification, and the opportunity to virtually map every other partial, sectoral or dimensional framework into the complete extent of the BIM Education Schema. The main BIM topics considered in BIM Schema v1.0 are:
- IPD Integrated Project Delivery
- Concurrent Engineering
- Lean
- Collaborative teamwork
- Value chain
- 2E EcoEficiency
- Relational contracts
- Common Data Environment
- Co-Design
- BIM roles
- Collaborative roles
- BIM Management
- BIM implementation
- BIM Execution
- BIM Uses
Other BIM topics can be added to this BS version as consequence of the cross competencies system of BIM Schema matrix. Content Creators can add other topics and relate with one or more units, in order to contribute to enrich BIM Schema.
Use of BIM Schema in Digital Transformation plans
BIM Schema is designed using a maturity matrix, to facilitate the creation of flexible and effective BIM E&T plans, as part of BIM digital transformation plans or BIP [BIM Implementation plan]. As the creator is a BIM Manager and BIM Consultant, his intention was a simple and easy to use system to standardize the overall design is intended to transform traditional AEC organizations into new digital AECO organizations, focusing on the critical importance of change people´s skills and abilities.
This global standardization is at the most importance for BIM managers and BIM consultants. Last ones are responsibles of the digital transformation of AEC traditional organizations, that is a complex process from the analogic industry to the new digital AECO industry. Workforce is critical for the success, specialy the introduction of new collaborative projects where a large number of organizations are interacting to deliver value chain for the clients. The Dilema is that once the transformation process started, is not possible to return without a severe business impact.
Resources available
- List of BIM management profiles
- List of BIM development profiles
- List of openBIM certified software
- List of BIM Uses and BIM units/courses
See also
- O2 BIM Education Schema content, the main content about BIM Schema and all the resources available in the consortium elearning platform [https://bim4ed.com/learn]
- BIM Schema 4 Creators, available in the consortium elearning platform [https://bim4ed.com/learn]
- BIM Schema 4 Users, available in the consortium elearning platform [https://bim4ed.com/learn]
- BIM ZERO (example of stakeholders/foundation course), available in the consortium elearning platform [https://bim4ed.com/learn]
References
[1] Penn State BIM Uses: https://bim.psu.edu/uses/
[2] bim4ed LMS: https://bim4ed.com/learn
[3] BSI certified software: https://www.buildingsmart.org/compliance/software-certification/certified-software/